The Chem Wizard

Organic Chemistry

Organic Chemistry is the study of chemistry in which the element Carbon (C) and Hydrogen (H) are bonded together as a compound such as methane (CH4), ethene and butyne - all of which are hydrocarbons and compounds that include both carbon and hydrogen and others:
Sulfur (S), Nitrogen (N), Oxygen (O), and/or Chlorine (Cl) and and/or any combinations of all of these.
The study of organic chemistry includes a system of naming these compounds which is called nomenclature.
Hydrocarbons are the default organic compound sub-group. They consist of compounds of carbons and hydrogens only. All of these sub-groups discussed in this page are called functional groups.
There are other kinds organic compounds and these are:
Alcohols, ethers, esters, carboxylic acid, aldehydes, and ketones. All of these sub-groups or functional groups are made of hydrocarbons bonded with oxygen (O) atoms. Many foods are made of these functional groups.
Amines are a sub-group or functional group that involve hydrocarbons bonded with nitrogen (N) atoms.
Amides are a sub-group or functional group with hydrocarbons bonded with both nitrogen (N) and oxygen (O) atoms.
Thiols are a functional group in which hydrocarbons are bonded to sulfur (S) atoms that are also bonded to one hydrogen each.
Haloalkanes are a functional group in which hydrocarbons are bonded to chlorine (Cl) atoms.





This hydrocarbon consists of four carbon atoms (gray), ten hydrogen atoms (white).
This alcohol consists of three carbon atoms (gray), eight hydrogen atoms (white) and one oxygen atom (red).
This amine consists of three carbon atoms (gray), nine hydrogen atoms (white) and one nitrogen (blue) atom.
This amide consists of three carbon atoms (gray), seven hydrogen atoms (white), one nitrogen (blue) atom,and one oxygen (red) atom double bonded to the carbon (gray) that is also attached to the nitrogen (blue)
This thiol consists of four carbon atoms (gray), ten hydrogen atoms (white) and sulfur (yellow) atom.
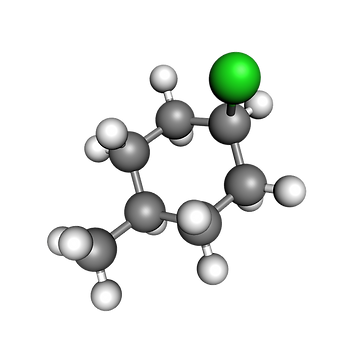
This haloalkane consists of seven carbon atoms (gray), thirteen hydrogen atoms (white) and one chlorine (green) atom.

Topics in Organic Chemistry
Functional Groups and Nomenclature
Chemical Properties of Organic Compounds
Common Reactions and Synthesis of Organic Compounds
Instrumentation in Organic Chemistry
Applications of Organic Chemistry